As an engineer’s blog, I’d like to share what I’m learning on a daily basis.
This time, the theme is AI Agents, which have been gaining significant attention in recent years.
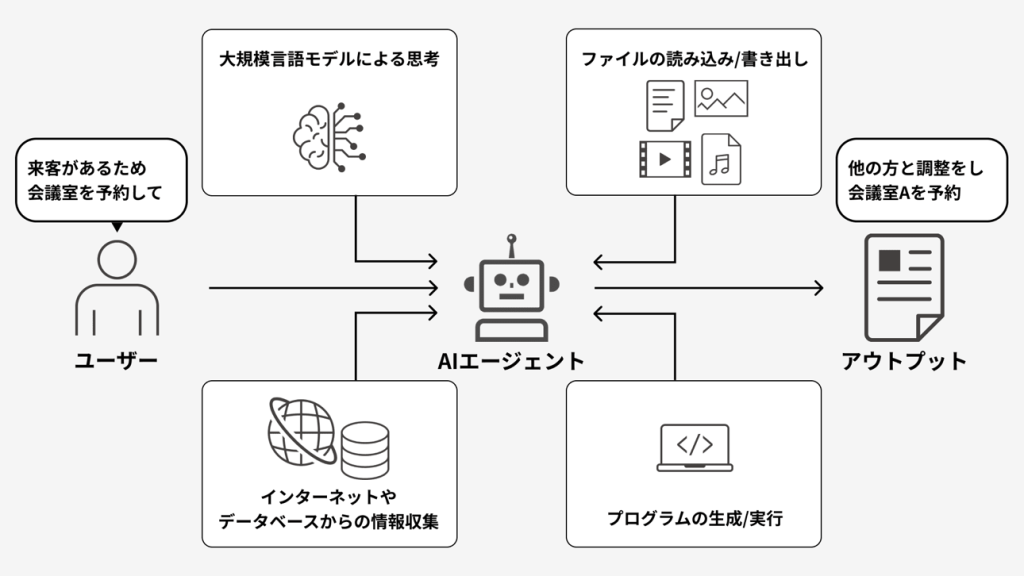
An AI Agent is an autonomous system capable of recognizing its surroundings, making judgments based on the situation, and taking action.
Unlike ordinary automation, its defining feature is the ability to flexibly handle tasks using learning and reasoning.
Recently, examples of incorporating AI Agents into work and system development using frameworks like ChatGPT and LangChain are increasing.
Translated with DeepL.com (free version)
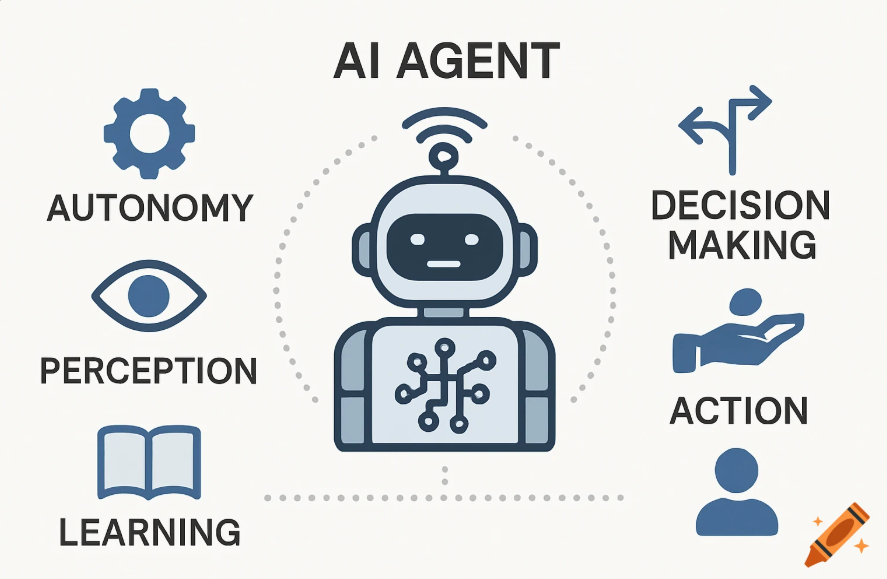
1.Basic Elements of an AI Agent
The AI Agent consists of the following four elements.
- Perception: Recognizing the environment and data (e.g., text analysis, sensor information)
- Reasoning: Making decisions based on knowledge and rules
- Action: Execute a task (e.g., API call, document generation)
- Learning: Accumulating experience and improving
Traditional programs only performed predetermined tasks, but AI Agents can flexibly adapt their actions based on the situation.
2.Representative Frameworks
① LangChain
- Features: Utilizes LLM (Large Language Model) to decompose and execute complex tasks.
- Strengths: Easy API integration, enabling automatic combination of search, calculation, and information organization.
- Usage examples: Document search agent, automated customer support responses.
② AutoGPT
- Features: When a goal is set, it autonomously plans and executes multiple tasks.
- Strength: Can determine next steps independently with minimal direction from others.
- Use cases: Automating research tasks, drafting blog posts.
③ BabyAGI
- Features: A compact autonomous agent that utilizes memory to continuously manage tasks.
- Strengths: Simple and lightweight, suitable for personal use and small-scale projects.
- Use cases: Daily to-do list management, automating information organization.
3.Use Cases
- Software Development: Support from Requirements Definition to Test Automation
- Business Operations: Streamlining customer support, scheduling, and research tasks
- Daily Life: Smart Home Control, Learning Support
These are not merely “tools,” but are expected to be “partners” that collaborate with humans to achieve results.
4.Future Outlook and Challenges
Outlook: Advancement toward “multi-agent systems” where multiple AI agents collaborate to solve problems as a team.
Challenges: Reliability, security, and ethical concerns (risks of misinformation and excessive autonomy).
This time, we introduced the basics of AI Agents and their potential applications.
Next time, we plan to share our hands-on experience building an AI Agent using LangChain and having it perform simple tasks, along with our impressions of using it. We’ll include code examples and results to explain, based on our experience, how it can be applied to business operations.
If you’re interested in AI Agents, be sure to tune in next time.

































